Glossary |
Aperture (DE: Blende) |
updated: 2021-08-10 |
 Aperture, or f-stops, is the relation between the area over which light can enter your camera or CMOS or CCD chip and the focal length of your lens.
Aperture, or f-stops, is the relation between the area over which light can enter your camera or CMOS or CCD chip and the focal length of your lens.
|
Aperture symbol |
Aperture Unit |
Formula |
|
B |
[none] |
B = Fob/d |
where:
Fob = focal length of the lens in [mm]
d = diameter of the lens or telescope in [mm]
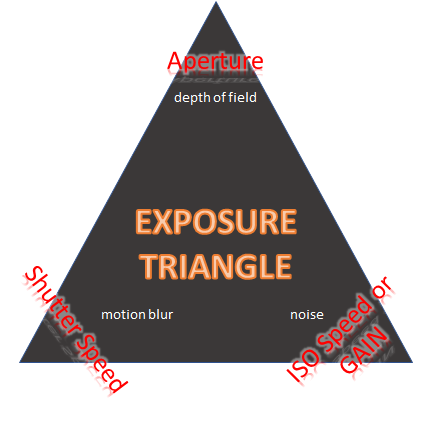
Other important factors of the exposure triangle are:
- Exposure time: has an impact on sharpness of moving objects
- ISO speed or gain: is the sensitivity and has an impact on the grain or noise
- (Filters: reduce the sensitivity and require changes in the exposure triangle)
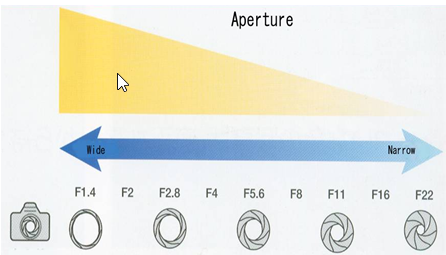 Lower f-stop settings (such as F5.6) have a larger diaphragm opening, allowing more light through the lens.
Lower f-stop settings (such as F5.6) have a larger diaphragm opening, allowing more light through the lens.
On the other hand, Higher f-stop settings (such as F11) have a smaller diaphragm opening, allowing less light through the lens
The aperture settings on cameras are commonly referred to as f-stops and have a specific numerical sequence, such as: F5.6, F7.1, F8, F11 and go in sqrt(2) sequence.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Simplify Your Help Documentation Process with a Help Authoring Tool
