|
PixInsight |
Step 10 (Optional)
|
updated: 2025-10-26 |
|
Purpose |
To bring more (false!) color into the image |
|
Activation |
Main step: Script > Toolbox > CreateHubblePaletteFromOSC |
|
Input |
any still linear, denoised star-less image from an OSC color camera |
|
Output |
a linear color image |
|
Previous Step |
or |
|
Next Steps |
|
|
|
General Description
The basic idea how to apply a Hubble palette to a one-shot color (OSC) image in PixInsight is to split the color image according to the wavelengths of the three important frequencies found in typical emission or reflection clouds.
|
Element |
Associated Color |
Wavelegth [nm] |
|
SII (Sulfur) |
Red |
672 |
|
Ha (or Hα, H-Alpha) |
Green |
656 |
|
OIII (Oxygen) |
Blue |
496 |
This can be done using the scripts available in PixInsight or online. These scripts split the images and, in the case of CreateHubblePaletteFromOSC, recombine the three separate black-and-white images at the end, followed by color adjustments (using e.g. the Curves Transformation process).
- Pre-processing and Data Acquisition (Implied)
- Narrowband Filters:
The ideal scenario for a Hubble palette is using separate H-alpha (Ha) and OIII filters with a monochrome camera, which are then combined into a SHO (or HOO,...) palette.
- OSC Data:
For a single-shot color (OSC) camera, the normalization scripts are designed to extract an approximation of H-alpha and OIII data from your broadband RGB image.
NOTE: The usage of narrow-band filters, such as the dual-band Optolong L-eXtreme filter, when shooting light frames, may lead to unwanted effects. This filter suppresses all wavelengths except Hα and OIII, blocking the SII wavelength.
Processing steps
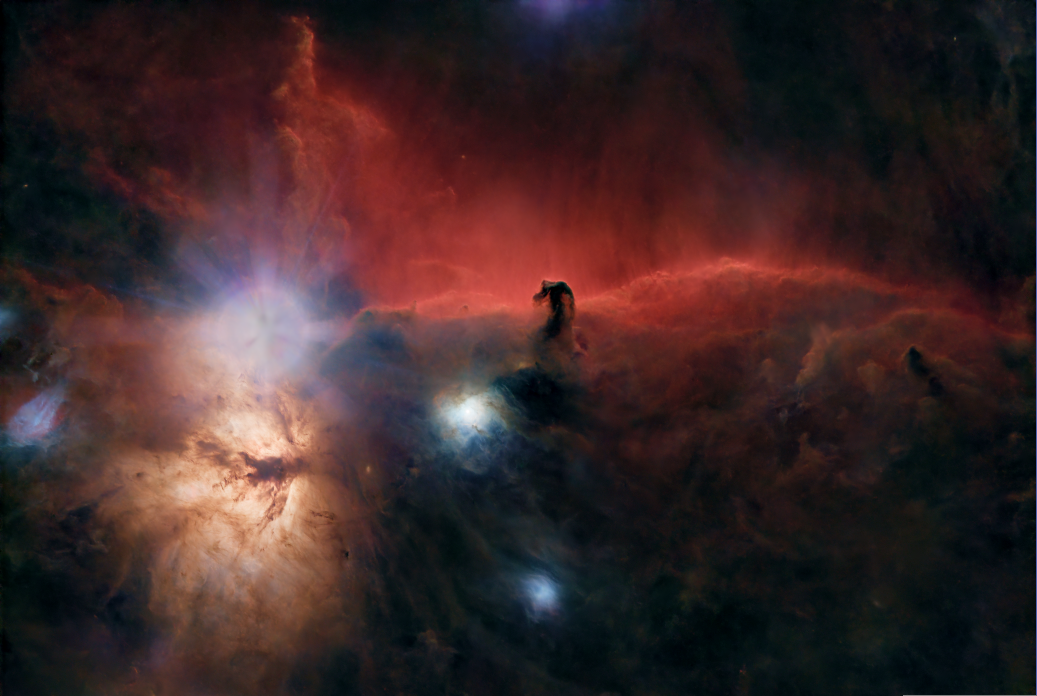
- Start with the starless image from step 6
|
Starless Image (identifier: Cloud, postfix: *_Cloud_HT_CT) |
|
|
- Apply a Normalization Script
Many scripts are available online that support this wavelength-based normalization.
Available Scripts:
|
Script |
Where? |
|
CreateHubblePaletteFromOSC provides different normalization options: |
Script > Toolbox > CreateHubblePaletteFromOSC |
|
HOONormalization_V8 |
|
|
SHONormalization_V8 |
|
|
HSONormalization_V8 |
|
|
HOSNormalization_V8 |
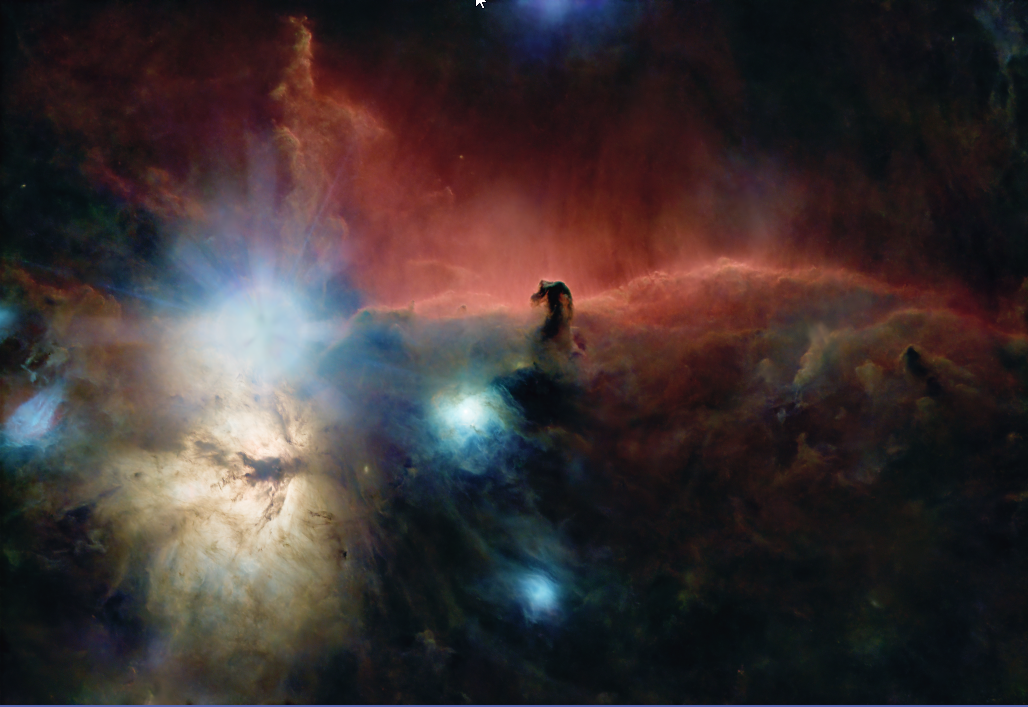
Example: Using the HOSNormalization_V8
|
Script HOSNormalization_V8 |
Resulting Image |
|
/* Normalize HOS data with Pixelmath - V8 by Bill Blanshan and Mike Cranfield */
Mode= 1 ; //<-- Data type, 0: linear, 1: Non-linear Lightness= 1 ; //<-- 0=OFF, 1=Original, 2=Ha, 3=SII, 4=OIII SCNR= 1 ; //<-- 0=OFF, 1=On Blackpoint= 1.00 ; //<-- Blackpoint range (0 to 1= min to med) SIIBoost= 1.00 ; //<-- Increase to boost SII OIIIBoost= 1.00 ; //<-- Increase to boost OIII HLRecover= 1.00 ; //<-- If highlights are clipped, increase >1 HLReduction= 1.00 ; //<-- If highlights are too bright, increase >1 Brightness= 1.00 ; //<-- Increase to stretch image /* Drag the bottom left arrow over to your HOS image Hope you enjoy!!! .... see next page |
|
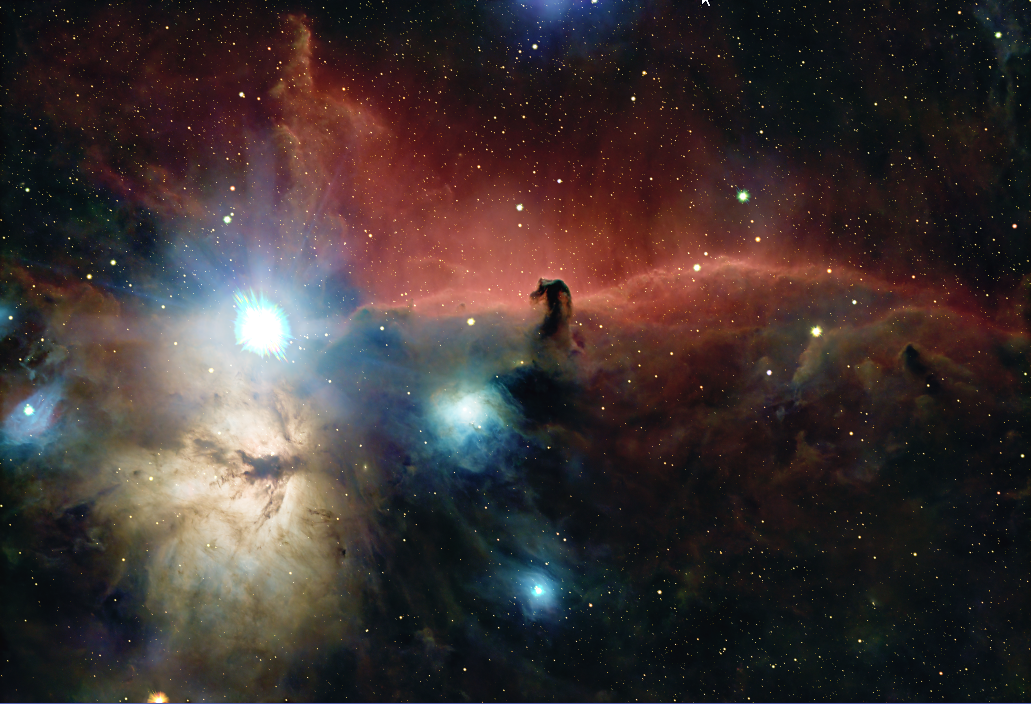
- Add Stars to Cloud image with PixelMath (save to *_MASTER_BX_NX_GX_HOS_Stars+Cloud)
|
PixelMath |
Resulting De-Linearized (stretched) Image |
|
|
|
Links:
.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Transform Your Help Documentation Process with a Help Authoring Tool