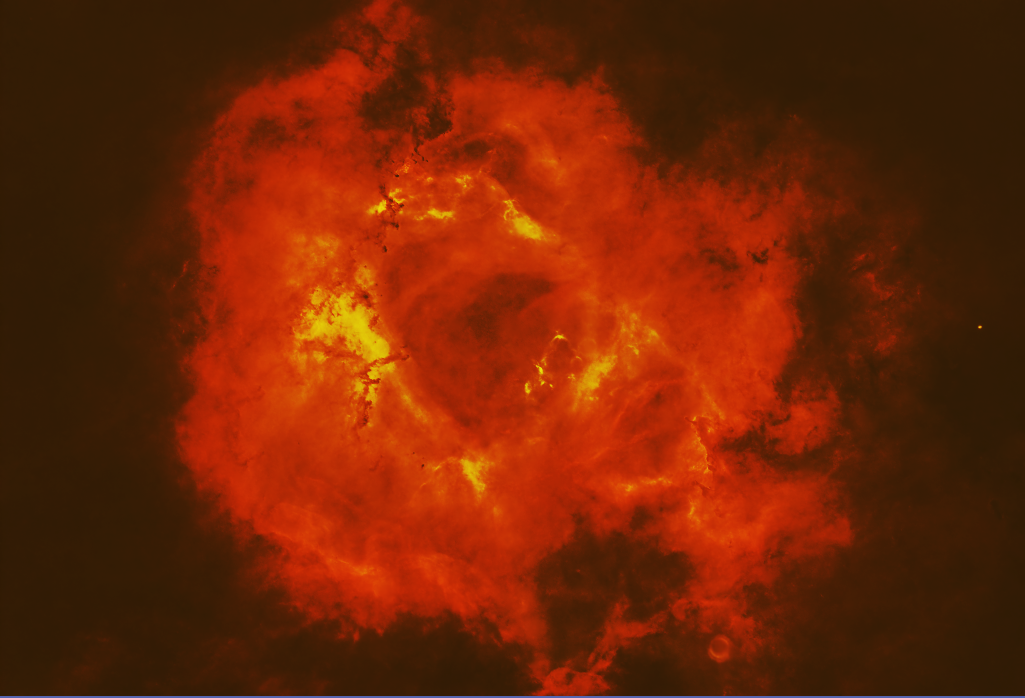
|
PixInsight - |
Hubble Palette Processing on Color Images from an OSC Camera |
updated: 2025-09-23 |
|
Purpose |
To bring more (false!) color into the image |
|
Activation |
Main step: Script > Toolbox > CreateHubblePaletteFromOSC |
|
Input |
any still linear, denoised star-less image from an OSC color camera |
|
Output |
a linear color image |
|
Previous Step |
|
|
Next Steps |
|
|
|
General Description
The basic idea how to apply a Hubble palette to a single-shot color (OSC) image in PixInsight is to split the color image according to the wavelengths of the three important frequencies found in typical emission or reflection clouds.
|
Element |
Associated Color |
Wavelegth [nm] |
|
SII (Sulfur) |
Red |
672 |
|
Ha (or Hα, H-Alpha) |
Green |
656 |
|
OIII (Oxygen) |
Blue |
496 |
This can be done using the scripts available in PixInsight or online. These scripts split the images and, in the case of CreateHubblePaletteFromOSC, recombine the three separate black-and-white images at the end, followed by color adjustments (using e.g. the Curves Transformation process).
- Pre-processing and Data Acquisition (Implied)
- Narrowband Filters:
The ideal scenario for a Hubble palette is using separate H-alpha (Ha) and OIII filters with a monochrome camera, which are then combined into a SHO (or HOO,...) palette.
- OSC Data:
For a single-shot color (OSC) camera, the normalization scripts are designed to extract an approximation of H-alpha and OIII data from your broadband RGB image.
Processing steps
- Open the the integrated linear master image from FBPP or WBPP from the alignment and integration process
(Postfix *_MASTER)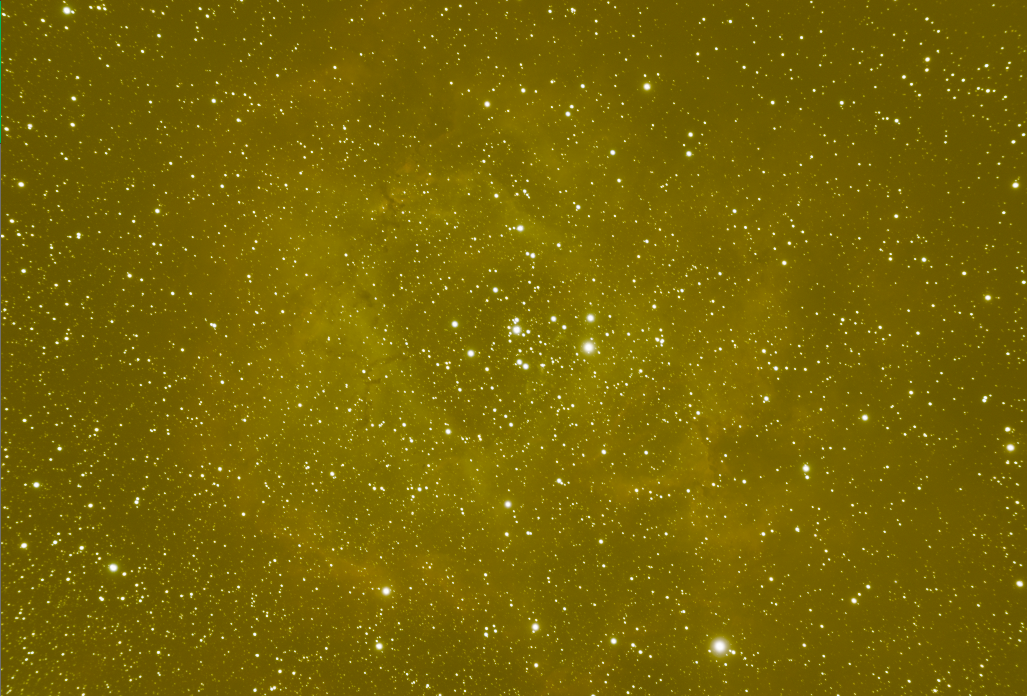
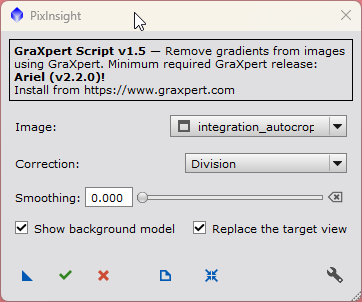
- Run GraXpert to (Script > Toolbox > GraXpert) to eliminate gradients:
|
GraXpert |
Resulting Image (postfix: *_GX) |
|
|
|
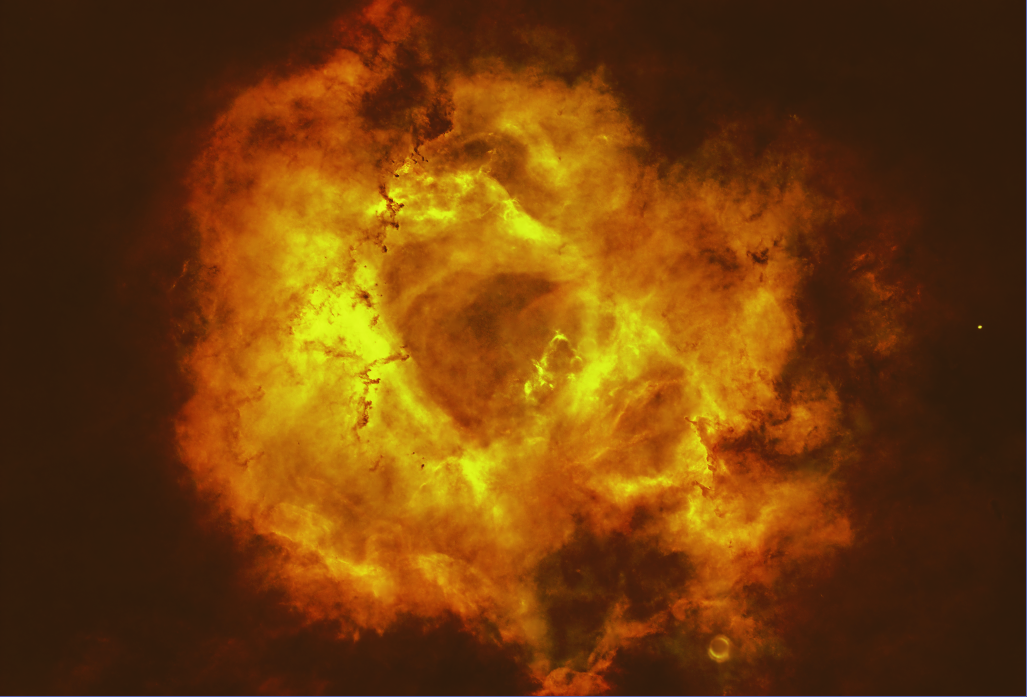
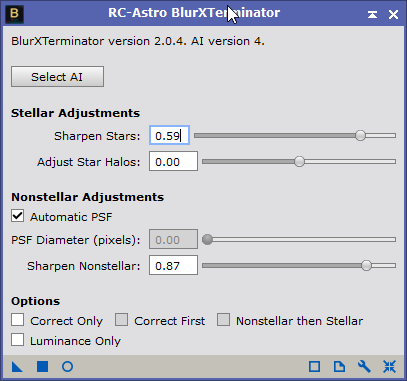
- Reduce blur and star size, e.g. RC-Astro BlurXTerminator (Process > Deconvolution > BlurXTerminator)
|
RC-Astro BlurXTerminator |
Resulting Image (postfix: *_BX) |
|
|
|
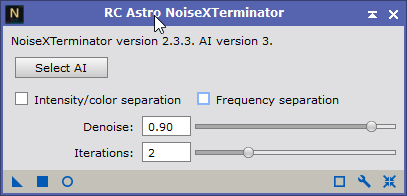
- Use the a Denoise script or process to reduce background noise like:
- EZ Denoise script (Script > EZ Processing Suite > EZDenoise)
- RC-Astro NoiseXTerminator (Process > Noise Reduction > NoiseXTerminator)
|
RC-Astro NoiseXTerminator |
Resulting Image (postfix: *_NX) |
|
|
|
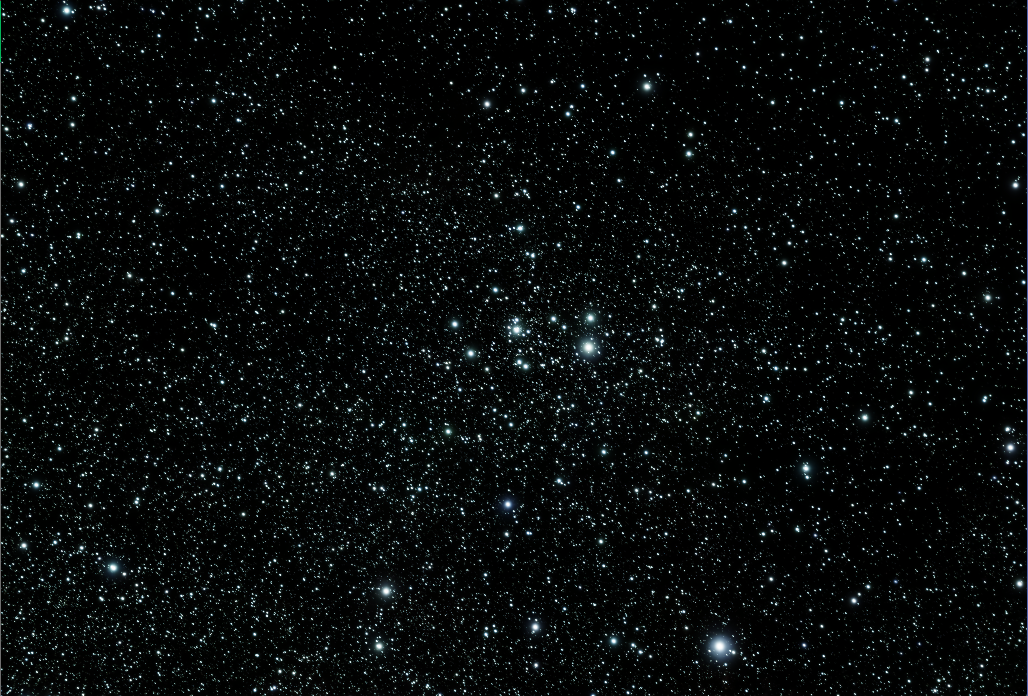
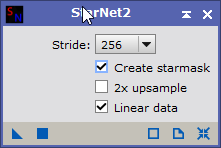
- Separate the nebula and the stars to create a starless image. You can do this using either:.
- StarNet2 (Process > StarNet2) with these options:
- or RC-Astro StarXTerminator (Process > Mask Generation > StarXTerminator)
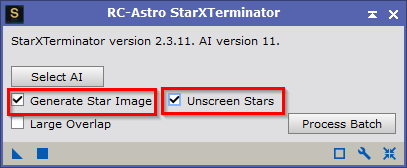
This creates 2 new images:
|
Starless Image (identifier: Cloud, postfix: *_Cloud) |
Star Mast (identifier: Stars, postfix: *_Stars) |
|
|
|
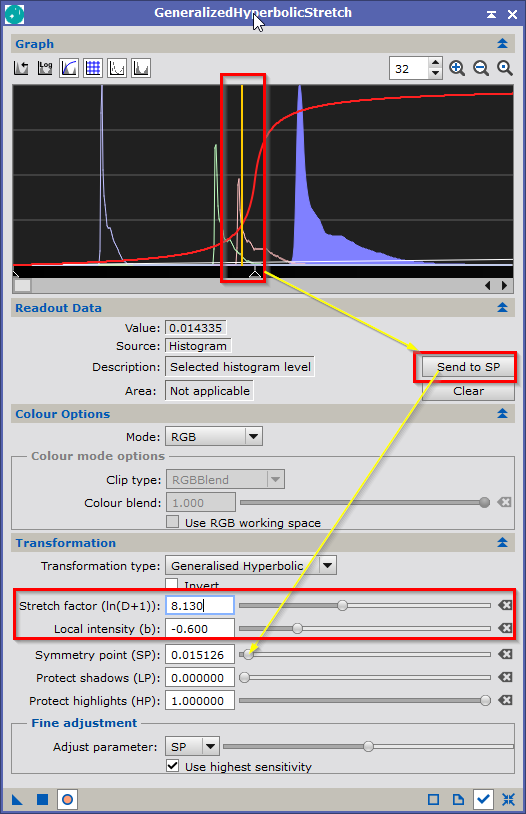
- Open GeneralizedHyperbolicStretch to unstretch the cloud image (Process > Intenisty Transformationy > GeneralizedHyperbolicStretch)
Set the transformation to "Linear," open the "Preview" window, and then drag the triangle to the right of the graph until the "Low Clip" starts to increase from 0.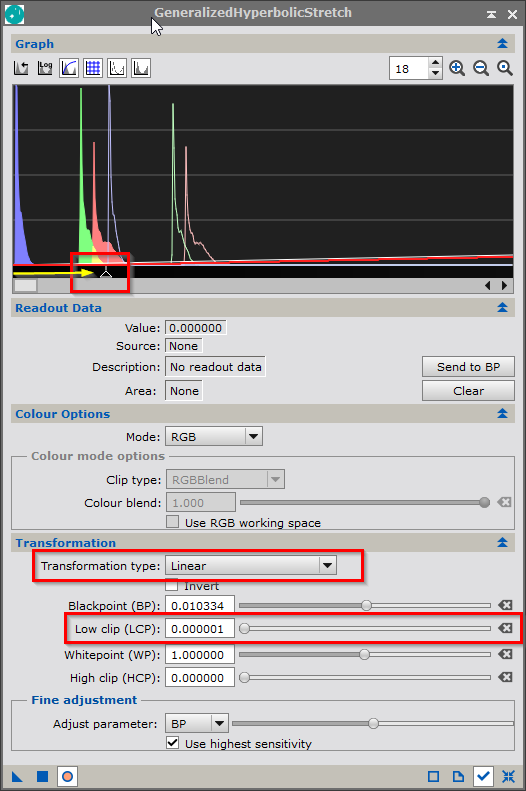
- Close the Preview and reset the GeneralizedHyperbolicStretch
- In GeneralizedHyperbolicStretch open the preview windows again and use the settings below.
Move the mouse pointer to the middle of the graph to see a yellow vertical line. This is the symmetry point. You can transfer this position to the symmetry slider by clicking the "Send to SP" button.The position of the symmetry point is crucial to image quality, which becomes apparent when you slide the stretch factor and local intensity sliders until a good image appears in the preview window.
|
GeneralizedHyperbolicStretch |
Resulting Non-Linear Image |
|
|
|
- Apply a Normalization Script
Many scripts are available online that support this wavelength-based normalization.
Available Scripts:
|
Script |
Where? |
|
CreateHubblePaletteFromOSC provides different normalization options: |
Script > Toolbox > CreateHubblePaletteFromOSC |
|
HOONormalization_V8 |
|
|
SHONormalization_V8 |
|
|
HSONormalization_V8 |
|
|
HOSNormalization_V8 |
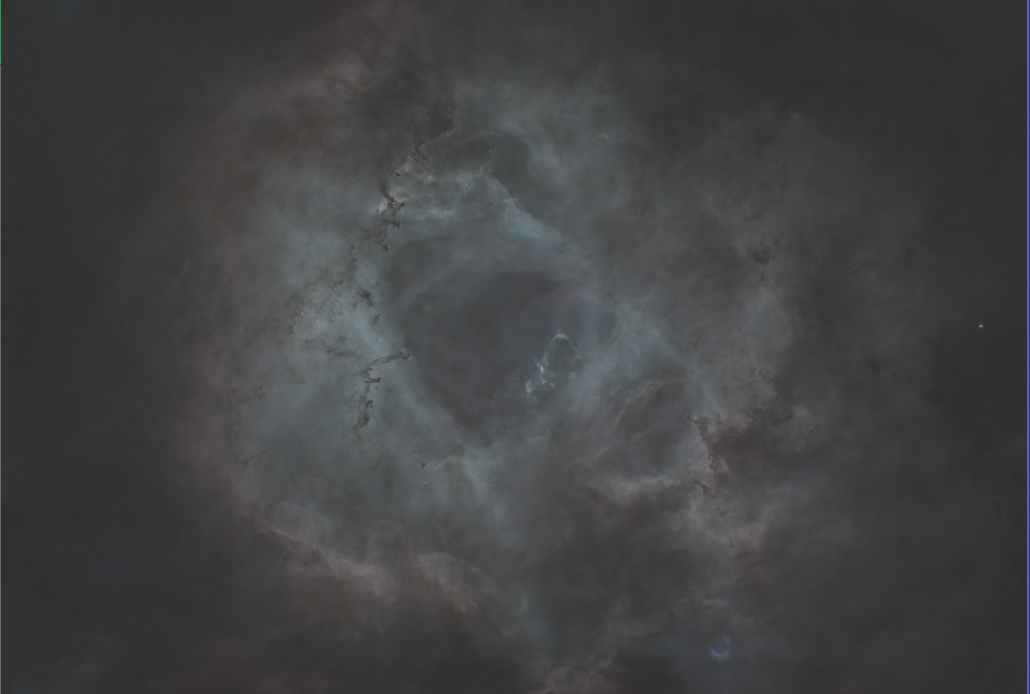
Example: Using the HOSNormalization_V8
|
Script HOSNormalization_V8 |
Resulting Image |
|
/* Normalize HOS data with Pixelmath - V8 by Bill Blanshan and Mike Cranfield */
Mode= 1 ; //<-- Data type, 0: linear, 1: Non-linear Lightness= 1 ; //<-- 0=OFF, 1=Original, 2=Ha, 3=SII, 4=OIII SCNR= 1 ; //<-- 0=OFF, 1=On Blackpoint= 1.00 ; //<-- Blackpoint range (0 to 1= min to med) SIIBoost= 1.00 ; //<-- Increase to boost SII OIIIBoost= 1.00 ; //<-- Increase to boost OIII HLRecover= 1.00 ; //<-- If highlights are clipped, increase >1 HLReduction= 1.00 ; //<-- If highlights are too bright, increase >1 Brightness= 1.00 ; //<-- Increase to stretch image /* Drag the bottom left arrow over to your HOS image Hope you enjoy!!! .... see next page |
|
- Use the Curves Transformation tool to adjust the colors according to your preference, then save with the postfix *_HOS.
(for some reason this image lacks a blue component...??)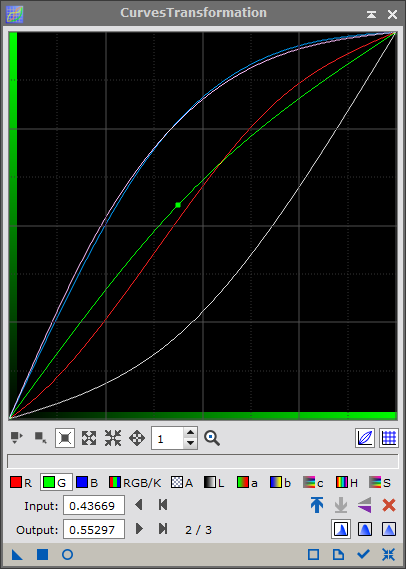
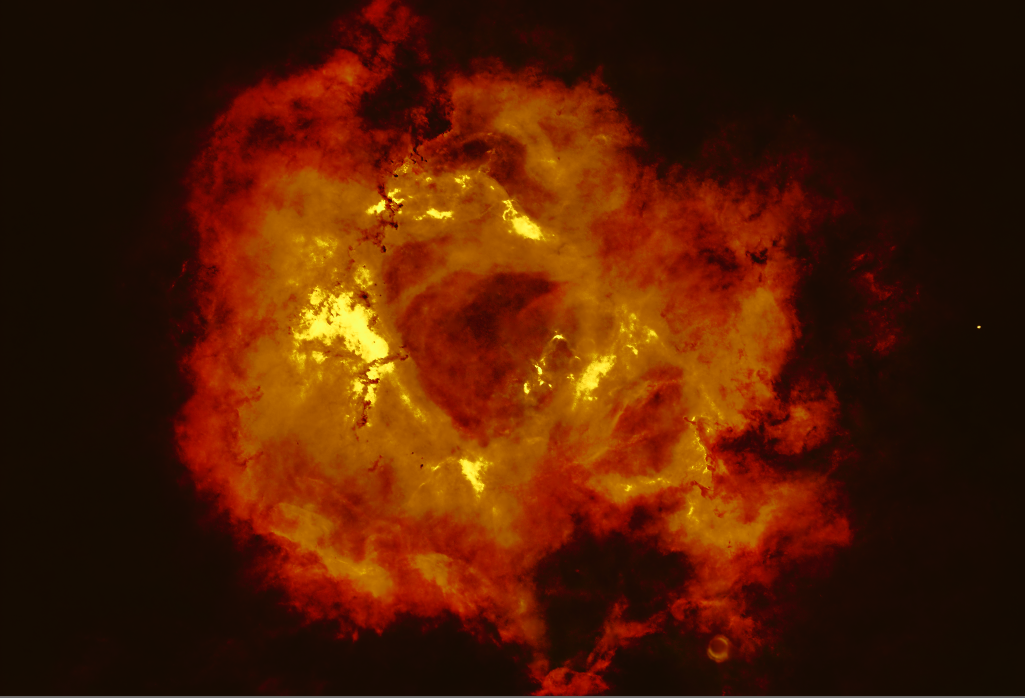
- Apply PCC (Photometric Color Calibration) on the Stars image to restore the original star colors
- Run Curves Transformation to increase the color saturation (in this case applied 3 times!)

- Apply HT on Stars
- Add Stars to Cloud image with PixelMath (save to *_MASTER_BX_NX_GX_HOS_Stars+Cloud)
Stars1 + Cloud1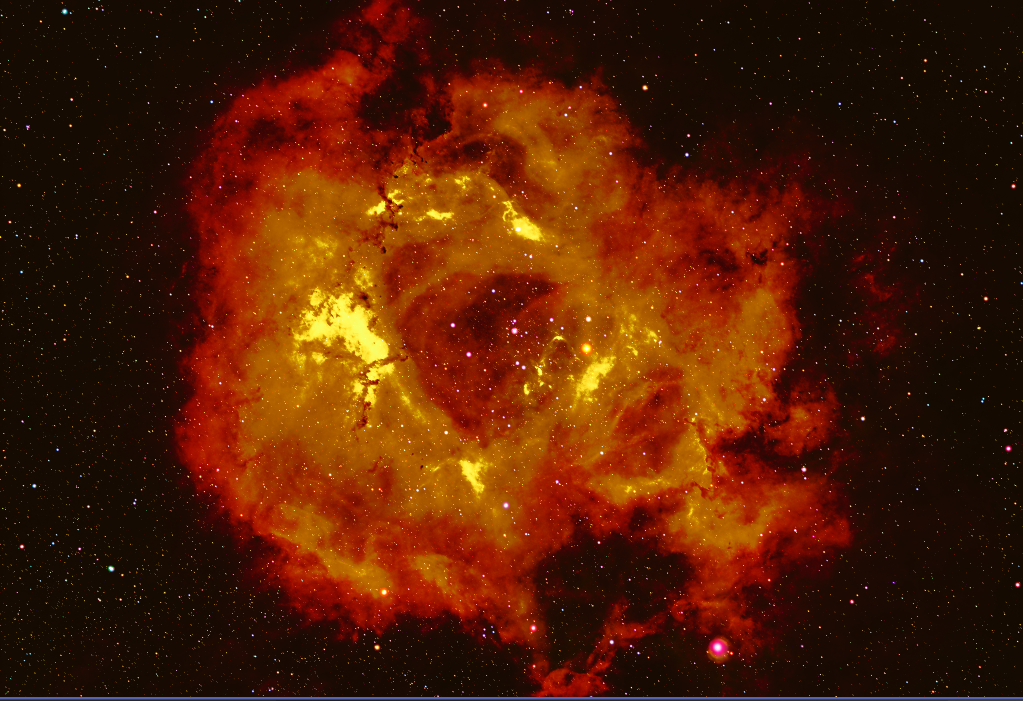
Links:
.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Transform Your Help Documentation Process with a Help Authoring Tool